Chapter wise IIT JAM Organic Chemistry : 2005 - Onwards
Click on the images to zoom and clear viewing.
Acidity of Particular Hydrogen Atom:
JAM 2006: The increasing order of the acidity of the hydrogen marked in italics
JAM 2005: Arrange
the following in the decreasing order of acidity of the hydrogen indicated in
italics:
CH3COCH3, CH3COCH2COCH3,
CH3OOCCH2COOCH3,
CH3COCH2NO2
Solution:
HO-, CH3COO-, PhO-, CH3O-
Solution: Nucleophilicity
refers to the ability to be a nucleophile. Greater is the extent of negative charge
over Oxugen greater nucleophilicity. The methyl group in methoxide ion pushes
electrons towards O atom and increases its nucleophilicity compared to
hydroxide ion. Now in phenoxide ion the negative charge is distributed between
ring carbon and on oxygen atom but in acetate ion the negative charge is
distributed between two oxygen atom which is more effective distribution
compared to phenoxide. Thus acetate ion has the lowest charge over O atom.
Hence the order is:
CH3O- > HO- > PhO-
> CH3COO-
Electrophilic Substitution Reaction
JAM 2006: The maor product of the reaction:
JAM 2005: The
rate of nitration of the following aromatic compounds decrease in the order:
Benzene, Pyridine, Thiophene, Toluene
Solution: Nitration
is an electrophilic substitution reaction. The difference between the calculated
energy of the nitro substituted structure and experimentally determined energy
is called the resonance energy. Lower is the resonance energy greater is the
reactivity towards nitration.
Thiophene has the lowest R.E of
29kcal/mol, hence it readily goes electrophilic substitution reaction compared
to the rest three. The rest three has almost same resonance energy but higher
is the electron density on the ring higher will be the reactivity. CH3
pushes electron towards the ring in toluene hence it is next more reactive, and
then comes benzene and then pyridine.
Thys the order is: Thiophene >
Toluene > Benzene > Pyridine
JAM 2005: For the reaction shown below if the concentration of KCN is increased four times the rate of reaction will be:
a) BrCH2CH(Br)CH=CH2
b) CH2=CH-CH2CH2Br
c) CH2=C(Br)-C(Br)= CH2
d) BrCH2CH=CHCH2Br
Solution: (d) At first one molecule of bromine is added to one of the double bond. The bromine on last carbon makes a cyclic transition state by pushing the next bromine out as bromide ion. That bromide ion attacks the next double bond, pi bond shifts and the product is formed as following:
Active methylene compound
JAM 2006: In the reaction sequence the X and Y are:
(+)CH3CH(I)CH2CH3 + NaI*
-----------> CH3CH(I*) CH2CH3 +
NaI
For this reaction, the relationship between kr and ki
is:
Solution:
Here ½ mole of (I) reacts with ½ mole of NaI* to produce ½ mole
of inverted product. Thus ½ mole of (I) and ½ mole of (II) produce 1 mole of
racemic mixture. Hence rate of racemization is twice of rate of incorporation.
Kr = 2ki
In the scheme shown above P,Q, R and S are:
IIT JAM 2005: Match the isoelectric point with the given amino acids.
H2NCH2COOH,
HOOCCH2CH2CH(NH2)COOH,
H2N(CH2)4CH(NH2)COOH
and 9.5, 6.0, 3.1.
Solution: Neutral amino acids having equal acidic and basic group will have pH 5.5 to 6.3. Thus the lysine (first one) should get the value of 6.0
Acidic amino acids having more acidic group than basic group will have pH around 3 and accordingly the second amino acid glutamic acid should have Isoelectric point of 3.1.
Basic amino acids having less acidic group than basic group will have pH 7.6 to 10.8 and accordingly the third amino acid lysine should have Isoelectric point of 9.5.
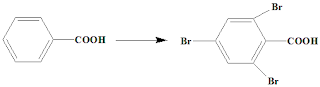
IIT JAM 2005: How may the following transformation be
affected? Indicate clearly the reagent / reaction condition in each step.
A. (Not involving
any functional group transformation of the COOH group in the starting material)
C.
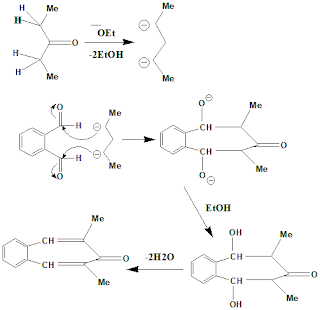
Solution:IIT JAM 2005: Write suitable mechanism

IIT JAM 2005: Rationalise
the following observations using suitable mechanisms.
A. Nitration of 4-t-butyltoluene gives 4-nitrotoluene as one of the products.
Solution: A stable tertiary carbocation is eliminated in exchange of hydrogen ion from nitric acid to regain the aromaticity, then usual nitration of toluene occurs.
Solution: In geometrical isomerism, a cyclohexane ring structure having upward-upward or dowm-down bisubstitution is considered Cis. In chair form the 1,2 or 1,4 bisubstitution is considered Cis if the substitutions are equatorial and axial to each other.
The Hofmann elimination becomes successful in the cis form because a hydrogen is present anti or trans to the aminehydroxide group which is not found in trans form.
C. PhMgBr and 2 moles of PhCHO react first in
dry ether and after acidic work up form PhCOPh and PhCH2OH.
Solution:
IIT JAM 2005:
a. Suggest a chemical method
for the separation of the mixture containing p-N.N-dimethylaminophenol and
p-aminobenzoicacid and give confirmatory test for phenol.














































Hi ! Please Do Not Spam in Message and Be Honest and Respectful.